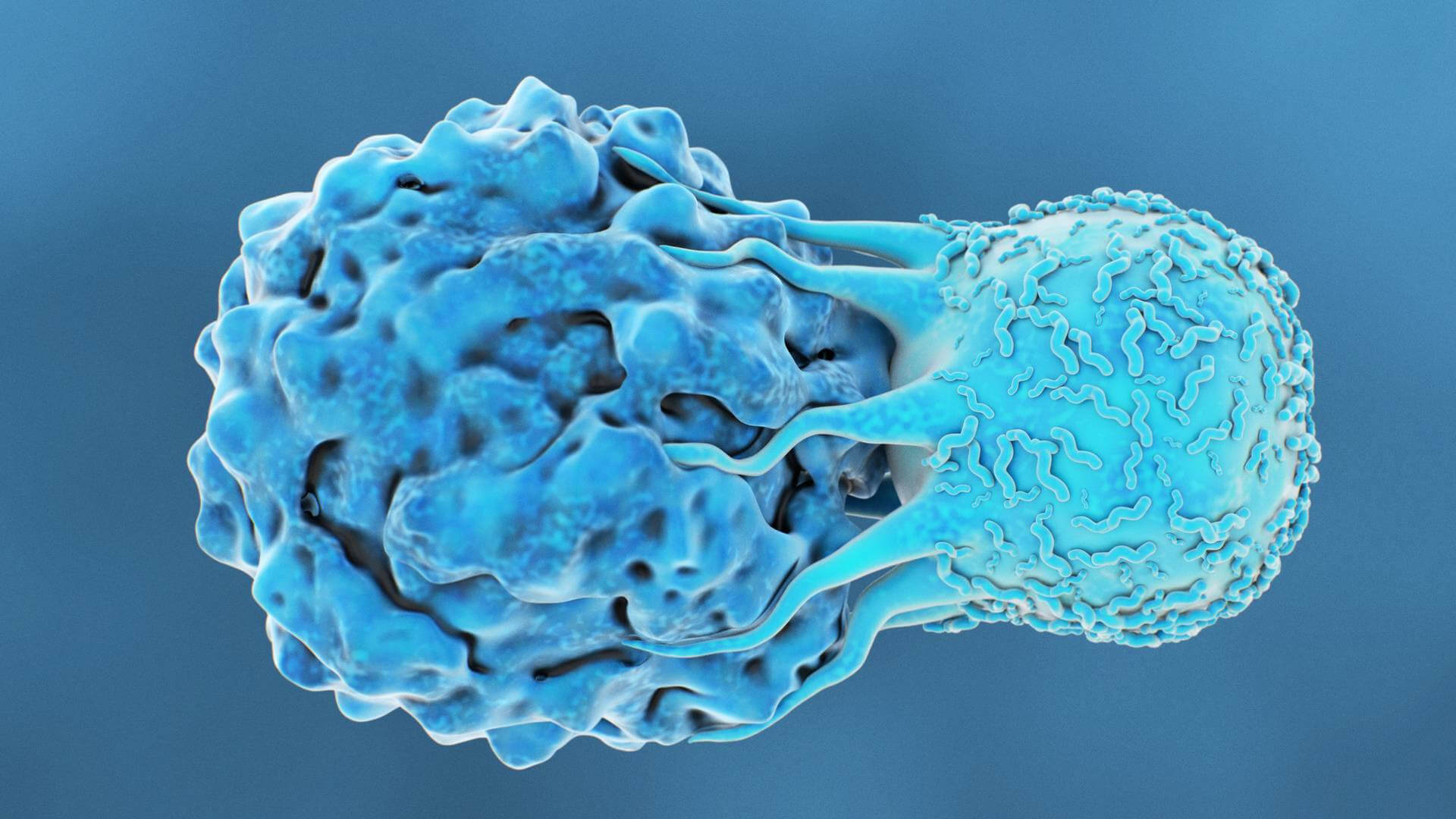
Ever heard of CAR-Ts? What does that mean anyway?
Chimeric antigen receptor T-Cell therapy!
What are T-Cells?
A type of white blood cell that is a part of the immune system. Two types of T cells exist – Cytotoxic T-cells and Helper T-cells. Helper T-cells notify and direct other cells to infection sites, while cytotoxic T-cells destroy infected cells. Each T-cell can only fight one type of infection and will clone itself to increase the numbers of immune cells fighting that individual infection. Cancer is one of the many types of infections that T-cells can target, making it useful for novel cancer therapies.
How do they become Chimeric T-Cells?
Leukocytes from the patient (autologous treatment) or from a healthy, compatible donor are collected (allogenic treatment), separated and expanded. The culture of collected cells are selectively expanded by use of a type of signaling protein called an interleukin and an antibody to specifically target the Leukocytes’ growth. Following purification, the leukocytes are transduced using a viral vector (retrovirus) containing the engineered chimeric antigen receptor sequence to make the final Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell aka CAR-T therapy. The resulting chimeric cell is carefully frozen and stored until use.
Note: the definition of chimeric in this context is containing tissue with two or more genetically distinct populations of cells.
What makes these therapies useful over currently available therapies?
The engineered chimeric antigen receptor is designed to fight very specific types of cancer by taking advantage of the unique surface chemistry of cancer cells. By arming the T-cell with a complimentary weapon to target cancer cell’s surface antigens, CAR-T therapy has higher selectivity to cells containing antigens that healthy cells lack. The therapy uses modified native biologic processes whereas chemo- and radiotherapies incur damage on non-specific surrounding tissues.
According to Wikipedia, there are currently six FDA-approved CAR-T Therapies. They are used for different types of leukemias and Lymphomas. Though their research started in 1987, it wasn’t until 2017 that the first two therapies were approved – Novartis’s Kymriah and Kite Pharma’s Yescarta. Challenges in production & manufacturing, cost of scaling and approval from regulatory agencies, as well as challenges in cold storage and transport, make it difficult for new CAR-T therapies to enter the market.
How does temperature play a role in manufacturing, storing, and administering the therapy?
From start to finish, temperature control plays a crucial role in CAR-T manufacturing. Selected viral vectors are purchased from cold storage banks and shipped on dry ice or by ice packs depending on specific needs. Those vectors are received and placed into internal cold storage at -80 °C to -190 °C. From cold storage, the cells are carefully thawed and taken into production environments where the cells and viral vectors are combined. Cell biochemistry happens in a single use style reactor, which must be temperature controlled to keep the cells alive and stable, usually at 37 °C for several days. Upon harvest, the cells are purified and aliquoted into vessels meant to transport the medicine to the patient, usually stored in cryopreservation for long periods of time, or at 2 to 8 °C for short holds or imminent usage. Some of the temperature-controlled processes are as follows:
· Lentivirus and retrovirus storage: -80 °C
· T-Cell growth conditions: 37 °C
· CAR-T Cells (transport): -80 to -190 °C
· CAR-T Cells (usage): 2 to 8 °C
· White Blood Cells storage: 2 to 8 °C
LAUDA Versafreeze and Mobifreeze are best in class solutions for cold storage and for transport between facilities. Versafreeze offers short pull-down times and maximum thaw times for best care for stored samples, low energy consumption and use of natural refrigerants, remote monitoring via LAUDA.LIVE, and intuitive options such as temperature monitoring units, water-cooling options, power-backup, as well as gas cooling back up for assurance that your investments are well guarded from accidental loss. Accessories include shelves, bins and boxes, but these freezers can also be used for large volume bio-process containers as well!
While Mobifreeze is not available on the US market yet (50 Hz only), LAUDA has manufactured a solution to reduce dry ice consumption for cold-chain transport. The LAUDA Mobifreeze chest freezer is a battery powered chest freezer on castors that can be used as a stationary freezer or to move samples between facilities for up to 4 hours at -80 °C, or one can simply plug the unit into a generator for mobile transport with longer times. Dry ice can pose a serious burn and asphyxiation risk, it can be a burden for planning due to fluctuations in price based on local fuel production, or by simply not using it fast enough and losing it to sublimination, money is being lost to the environment. Pay attention to LAUDA news to see if Mobifreeze is in your region yet, and get ready to start saving money on dry ice, lower your insurance premiums associated with hazardous environments and switch to a more eco-friendly solution to cold-chain transport.
Our TCUs and wet lab products are used every day globally in many bioprocesses surrounding cell therapy manufacturing:
· LAUDA Integral or Ultracool – Intelligent cooling and heating or general machine cooling for plate freeze thaw units for controlled thawing of bulk material in process containers or bioprocess bags.
· LAUDA Variocool, Integral, and UltraTemp – Precision control of reactor jacket temperatures where cells are expanded and transduced or in other situations where the CAR-T cell media is formulated and aliquoted for distribution. Trust LAUDA with keeping your investment stable while growing.
· LAUDA GFL, Microcool, Loop, Eco and Pro – Assisting benchtop chemistry with low volume thawing via our precision static and shaking baths, benchtop chillers and process heaters, chilling fractionation trays while chromatography is taking place, or with powerful shaking tables for mixing buffers or dissolving solids in solvents. Innovative technology for small scale, eco friendly chemistry like F-Gas free Peltier chillers.
· LAUDA has it all – worth mentioning but too many uses to list? We sell water stills for high purity water, tissue floats for histology, evaporator baths, thermoelectric chillers, and plant/commercial solutions from -150 °C to +550 °C.
This post was authored by Christopher Sebastiano, Southeast Sales Manager at LAUDA.
