Botanical Extraction
LAUDA Supports Botanical Processors
Temperature control solutions for cannabis and hemp processing. Industry insight supported by in-house engineering teams and interdisciplinary experience.

Distillation
Molecular distillation is used to separate and refine the crude oil from extracted biomass by removing the undesired volatile, super-heavy and pigment components. Vacuum assisted molecular distillation using LAUDA process thermostats allow distillation to proceed at a high degree of precision for (0.01 to 0.05 K) enhanced R&D and repeatability of processes. LAUDA’s high precision also lends itself to assuring you that your distillation temperatures never overshoot the desired set point, potentially harming the profile of the distillates being manufactured. And LAUDA’s reliability ensures that they will stand up to the long hours and harsh environments that distillations take place in, keeping your investment running and profitable. Distillates can be further refined into isolates, depending on the cannabinoid, further purified for API use or formulated into CPG products such as vaporizers, edibles, topicals, tinctures, tablets, and more.

Winterization
Winterization removes undesired non-polar compounds from the biomass, generally fats, lipids, and waxes. The winterization process depends on taking advantages of polarity differences in solvent and the unwanted fat and lipid compounds, which allows partial solubility in ethanol while warm and a sharp decrease in solubility when cooled. At -40 °C, a large amount of precipitated fat can be filtered out across most types of filters. Processers may choose to hold their winterization loads at colder temperatures for longer periods of time, as low as -80 °C for 24 hours in reactors and perform multiple filtrations. This important process ensures that your final product is as pure, visually clear and enjoyable as possible. LAUDA Integral process thermostats have a temperature range of -90 to +320 °C, making it the perfect partner for reactor chemistry, like the winterization process. Take it a step further and use our LAUDA.Live app to monitor your winterization temperatures remotely, to time your filtration and downstream processing with certainty.

Extraction
The extraction process is employed to extract cannabinoids like THC and CBD, as well as other valuable compounds like terpenes from biomass. The process may use different solvents or combinations of solvents, including LPG (butane, propane, isobutane), ethanol, CO2, and water. The biomass is soaked in the solvent and separated from the solvent by light heat. The biomass in this stage is kept at low temperatures to reject unwanted compounds from the extracts, like chlorophyll, to reduce the downstream purification burden or to produce a product that can be immediately packaged and sold. While dry ice is sometimes used to cool columns, some processors choose to employ a reliable and powerful Integral process circulator to hold their extraction columns as low as -90 °C and save money in the long term. The Integral product line features dedicated heaters for evaporating solvent and ultra cold chillers to power systems of all sizes.

Decarboxylation
Decarboxylation, a fundamental process in cannabis, involves a controlled heating of flowers or the THC-A oleoresin to release a carboxylic acid as CO2, making the compound psychoactive. CBD-A can similarly be decarboxylated, and is routinely done as part of the process in making CBD isolate, but does not change the psychoactive properties of the compound. The decarboxylation process reduces the compounds mass by about 12%, which leads to a reduced final load weight, depending on the crude extract’s purity. There are a few methods to decarboxylation: Hot plates or small short path distillation units for small loads, rotary evaporators and vacuum ovens for medium loads, and large reactors at 50% capacity for large batches. LAUDA products can be employed in many parts of the decarboxylation process, including running the heating for the reactor jackets, or cooling the condenser coils, ensuring no terpenes are lost and that your laboratory space remains free of noxious fumes. Our Integral and PRO product lines have the power and pumping speed to keep up with these demanding processes, with process programmability, an available range of -90 to 320 °C and power where it’s needed.
Excellent Service & Warranty
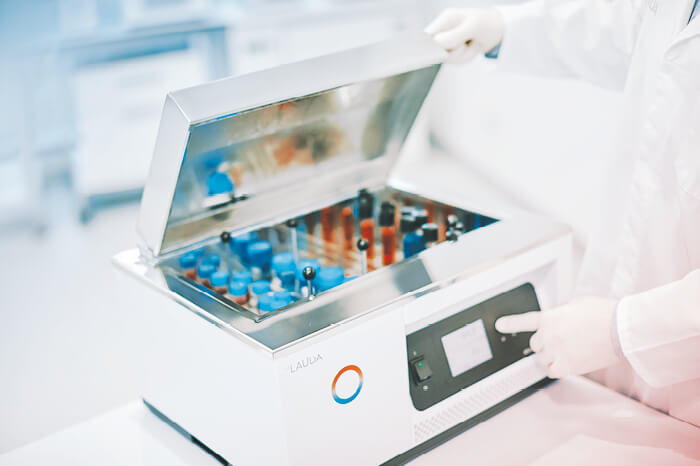
Water baths for variable use in biological, medical or biochemical laboratories for temperatures from 25 to 100 °C. Shaking water baths from 10 to 99.9 °C for the lab.
Shaking water baths of the LAUDA Hydro series move samples in the laboratory with a linear or orbital shaking movement, depending on the model. LAUDA Hydro shaking water baths are reliable companions for continuous operation in daily laboratory work.

Application examples
- Bacteriological examinations
- Molecular biology
- Demulsibility studies
- Processing chemical reactions
- Thawing
- Metallurgical analysis
- Incubation of microbiological assays
- Warming Reagents
- Environmental studies
- Food processing (QC)
- Water quality research
- Cytochemistry
Working temperature min.
25 °C
Working temperature max.
100 °C
Water baths for variable use in biological, medical or biochemical laboratories for temperatures from 25 to 100 °C. Shaking water baths from 10 to 99.9 °C for the lab.
Shaking water baths of the LAUDA Hydro series move samples in the laboratory with a linear or orbital shaking movement, depending on the model. LAUDA Hydro shaking water baths are reliable companions for continuous operation in daily laboratory work.

Application examples
- Bacteriological examinations
- Molecular biology
- Demulsibility studies
- Processing chemical reactions
- Thawing
- Metallurgical analysis
- Incubation of microbiological assays
- Warming Reagents
- Environmental studies
- Food processing (QC)
- Water quality research
- Cytochemistry
Working temperature min.
25 °C
Working temperature max.
100 °C
NEWS & LAUDA BLOG:
Keep up to date with our products, industry news, and informational articles.
Thermal Management in Digital Printing Presses
In digital printing presses, effective thermal management is critical to maintaining optimal performance and ensuring high-quality print outputs. These systems generate substantial heat through various processes, making precise temperature control essential to prevent...
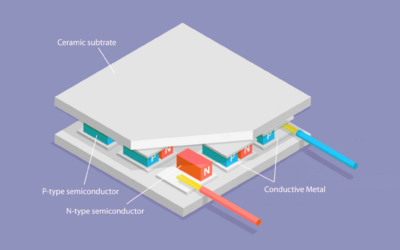
Thermoelectric Technology in Semiconductor Manufacturing
The semiconductor industry is continuously evolving, with environmental sustainability and space efficiency driving innovation. Among the technologies making significant strides is thermoelectric temperature control—a solid-state solution that combines rapid, precise...
Thermal Dynamics in Motion: Addressing Thermal Challenges in ICE, BEV, and FCEV Systems
The automotive industry is racing toward a future defined by electrification, hydrogen power, and smarter engineering. With these advancements come new challenges—particularly in thermal management. As powertrains evolve, so do their cooling requirements. This article...